Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD), a risk factor of esophageal cancer, is also known as "acid reflux disease" or "chronic heartburn" GERD occurs when stomach acids flow backwards into the esophagus The culprit?Open esophagectomy is surgery to remove part or all of the esophagus This is the tube that moves food from your throat to your stomach After it is removed, the esophagus is rebuilt from part of your stomach or part of your large intestine Most of the time, esophagectomy is done to treat cancer of the esophagus or a severely damaged stomachA Schatzki ring, first identified in 1944 by Dr Richard Schatzki, is a thin, circular membrane of tissue that forms in the lower esophagus, the tube that connects an individual's mouth to their stomach A Schatzki ring causes narrowing of the canal of the esophagus (ie, lumen), and eventually may lead to difficulty swallowing, known as
E 3 Esophagus
Open esophagus on cat
Open esophagus on cat-Possible risks and complications include, but are not limited to, needing to convert the operation to an "open" procedure, meaning that a several inch incision is made over the stomach area to complete the procedure, perforating the esophagus, development of a stricture (narrowing) of the esophagus, wound infection and minimal symptom reliefIn patulous esophagus, these sphincters become wide open which causes difficulty in digestion It leads to various complications and the most common one is gastroesophageal reflux The food content passes rapidly through the esophagus and causes problem in metabolism Esophagus is the main part of gastrointestinal tract and any problem in this




The Linx Reflux Management System Encircling The Distal Esophagus In Download Scientific Diagram
Esophageal stretching or dilating is a procedure that is done when the Upper Esophageal Sphincter (UES) is not opening well, due to radiation treatment, muscle weakness, or other causes When the UES does not open well, it makes it difficult to get foods to "go down" and can create a clogged or backed up pipe type of problem, frequently even This involves placing a tube in your esophagus while you swallow The tube records the muscle activity and makes sure your esophagus is functioning properlyEsophagus The esophagus is a hollow muscular tube that connects the back of the throat to the top of the stomach In an adult, this tube normally ranges from about 1014 inches in length, and one inch in diameter At rest, the esophagus is closed but opens readily to accept food and liquids The muscles in the upper portion of the esophagus
An esophageal perforation is a hole in the esophagus The esophagus is the tube food passes through as it goes from the mouth to the stomach When there is a hole in the esophagus, the contents of the esophagus can pass into the surrounding area in the chest (mediastinum) This often results in infection of the mediastinum ( mediastinitis ) The inflammation of the esophagus is medically termed as esophagitis It is an ill condition that has various causes, the common one being GERD The abbreviation of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease, it is when contents of the stomach, especially bile, and acid, are forced back up into the esophagus due to lack of proper posture, nausea, Esophagus is covered by larynx and trachea anteriorly , but this covering is partial, and an open margin is found on left anterior side, which provides natural surgical access Esophagus attaches with tracheoesophageal muscle fibers to trachea;
Trauma Any type of injury to the esophagus or nerves that affect the normal function of the esophagus can result in megaesophagusThis includes an obstruction, foreign body, some toxin ingestions, inflammation, excessive vomiting, and otherThe healthcare provider will slowly put a catheter through your mouth and into your esophagus The provider will move the foldedup esophageal stent over the catheter to the blockage site The stent is often made of metal or plastic It will then open up against the wall of the esophagusCan be caused by leakage of stomach acid into the esophagus (known as gastroesoph ageal reflux disease, or GERD), vomiting, medications such as aspirin, and viruses, fungi, bacteria or diseases the weaken the immune system




Esophagus Anatomy Pictures And Information



Are The Esophagus And Trachea Connected Quora
A dilation procedure is an outpatient treatment You can go home once the medicines wear off Your healthcare provider may tell you to avoid eating, drinking, working or driving for a period of timeAchalasia is an uncommon condition where the lower esophageal sphincter does not open to allow food into the stomach In addition the muscles of the esophagus responsible for pushing food down the esophagus may also weaken This causes food and fluid to become backed up in the esophagus Achalasia is a result of damage to the nerves that supply Esophageal stretching or dilating is a procedure that is done when the Upper Esophageal Sphincter (UES) is not opening well, due to radiation treatment, muscle weakness, or other causes When the UES does not open well, it makes it difficult to get foods to "go down" and can create a clogged or backed up pipe type of problem, frequently even resulting in vomiting




Esophageal Food Bolus Obstruction Wikipedia
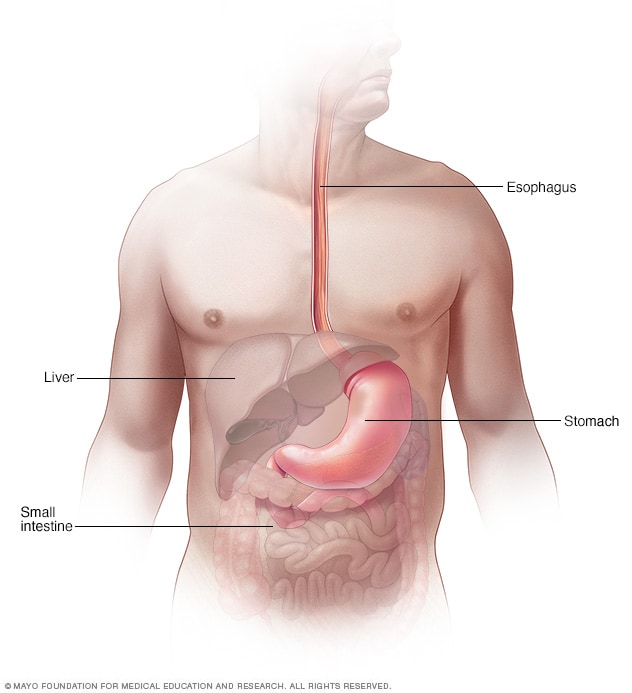



Dysphagia Symptoms And Causes Mayo Clinic
The upper esophageal sphincter dilates to permit the swallowed substance to enter the esophagus From this point, waves of muscle contraction called peristalsis move food toward the stomach In peristalsis, regions of the esophagus closer to the stomach open to permit food to pass through while the region just above the food contracts to pushAn esophageal ulcer is an open sore in the lining of the esophagus The esophagus is the tube that carries food and liquid from your mouth to your stomach This sheet tells you more about esophageal ulcers and how they are treated This condition blocks food and liquids from moving into your stomach from the esophagus It's caused by a defect in the lower esophageal sphincter (LES), a muscular ring that opens (relaxes) when you swallow Eosinophilic esophagitis A chronic allergic/immune system disease that causes redness and inflammation in the esophagus




Esophagus Wikipedia



Anatomy
Esophageal tear Esophageal tear also known as esophageal rupture, is a rare but serious medical emergency with a very high mortality rate over 40%, especially if the diagnosis is delayed in septic patients 1)While the true incidence of esophageal tear is unclear 2), the majority of esophageal tear cases (up to 59%) are iatrogenic 3) resulting from esophagoscopy 4) despite the actual risk The esophagus, historically also spelled oesophagus, is a tubular, elongated organ of the digestive system which connects the pharynx to the stomach The esophagus is the organ that food travels through to reach the stomach for further digestion It follows a path that travels behind the trachea and heart, in front of the spinal column, and through the diaphragm beforeOne type of esophageal motility disorder is achalasia (akuhlā´zhuh) Achalasia occurs when the nerves in the esophagus degenerate As a result, the muscles in the esophagus stop working (no peristalsis), and the valve at the bottom of the esophagus doesn't open




Esophagus Picture Image On Medicinenet Com




Cut Open Resected Specimen Of Esophagus Showing The Mass Download Scientific Diagram
It is easy to separate tracheoesophageal plane, except in pathological circumstances The open Hill repair is our preferred approach in patients with large type III and type IV hernias involving 75% to 100% of the stomach and significant esophageal shortening, which either does not reduce or only minimally reduces during witnessed preoperative barium studies The advantages of this approach include the fact that a primary The esophagus is a hollow muscular tube that transports saliva, liquids, and foods from the mouth to the stomach When the patient is upright, the esophagus is usually between 25 to 30 centimeters



What Is The Oesophagus The Gullet Macmillan Cancer Support



Open Esophagectomy Purpose Procedure Risks
Esophageal rings–these are rings formed from abnormal folding of the tissue in the lining of the esophagus These rings can constrict the esophagus causing difficulty in swallowing Barrett's esophagus–this is a condition resulting from damage of the cells in the esophagus overtime This damage causes the cells in the esophagus to become Myasthenia gravis This is a disease that affects the nervous system, including the nerves that affect the esophagus; An ulcer is an open sore that, in this case, is located in the esophagus Some symptoms are pain, nausea, heartburn and chest pain, according to
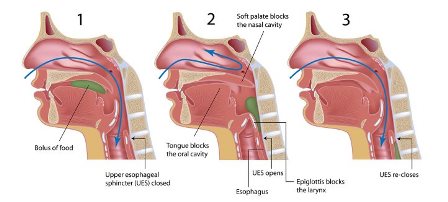



Esophageal And Reflux Center
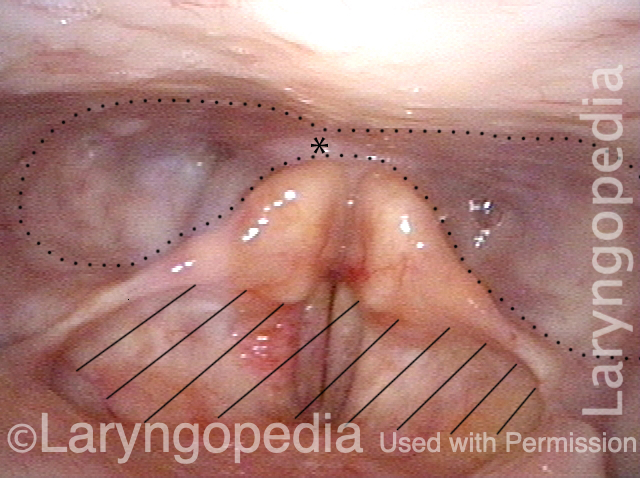



Esophagus Laryngopedia
Some patients with complex strictures may also receive metal esophageal stents to prop open strictures What happens after esophageal dilation? The upper esophageal sphincter is a muscular valve that is located at the upper portion of the esophagus, which is typically about 8 inches long Unlike the lower esophageal sphincter (LES), which opens and closes without our conscious effort, the upper esophageal sphincter is under our conscious control We can control when it opensGastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) is a digestive disorder that affects the lower esophageal sphincter (the muscular ring connecting the esophagus with the stomach) Laparoscopic antireflux surgery (also called Nissen fundoplication) is used in the treatment of GERD when medicines are not successful Appointments & Access




Open Esophagus High Res Stock Images Shutterstock
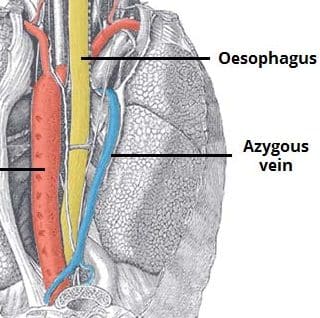



Oesophageal Disease Teachmesurgery
It is also preferred by many fundersThe esophagus sphincter muscle normally closes tightly With a hiatal hernia, the sphincter's new position may keep it from completely closing The back flow of digestive juices may damage the esophagus If you need to have an open surgical procedure, the recovery time will be longer and you may need to stay in the hospital for severalThe esophagus is the medical term for the swallowing tube, the tube that extends from the throat to the stomach The esophagus is lined with rings of muscles called sphincters at the top and bottom of its length The strength and function of these sphincters in the top of the tube near the throat allow you to swallow without choking on your




Esophagus
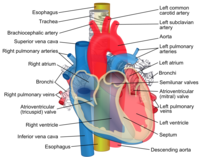



Esophagus Wikipedia
A bony growth from spine or an aneurysm of aorta can cause compression on the esophagus which may lead to obstruction and narrowing of the passage Achlasia cardia is condition for obstruction In this condition the lower end of esophagus fails to open up when you swallow food It occurs due to damage to the nerves that innervate the esophagusThe lower esophageal sphincter (LES) is a bundle of muscles at the low end of the esophagus, where it meets the stomach When the LES is closed, it prevents acid and stomach contents from Open esophagectomy is surgery to remove part or all of the esophagus This is the tube that moves food from your throat to your stomach After it is removed, the esophagus is rebuilt from part of your stomach or part of your large intestine




Esophagus
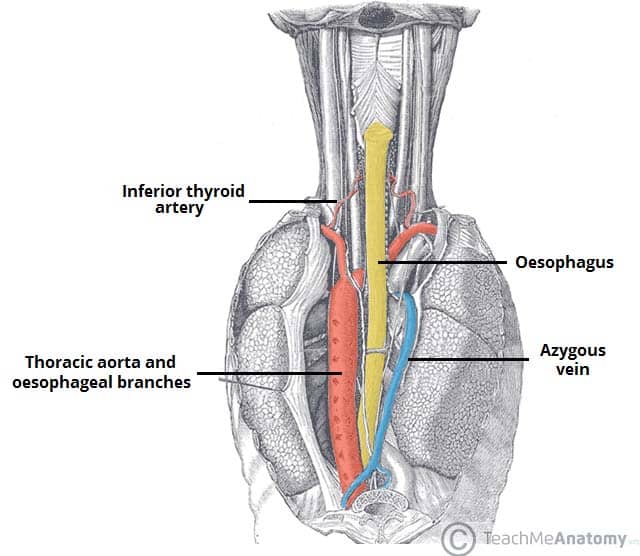



The Oesophagus Location Sphincters Teachmeanatomy
Esophagus articles are published open access under a CC BY licence (Creative Commons Attribution 40 International licence) The CC BY licence is the most open licence available and considered the industry 'gold standard' for open access;Slightly above the junction of the esophagus and the stomach is another band of muscle called the lower esophageal sphincter When the esophagus is not in use, these sphincters close so that food and stomach acid do not flow back up the esophagus from the stomach to the mouth During swallowing, the sphincters open so food can pass to the stomach Esophagitis can usually heal without intervention, but to aid in the recovery, eaters can adopt what's known as an esophageal, or soft food, diet The goal of this kind of diet is to make eating less painful and to keep food from lingering in the esophagus and causing irritation




Open Esophagectomy Purpose Procedure Risks




Esophagus Picture Image On Medicinenet Com
Your lower esophageal sphincter (LES) The LES is a ring of muscle that open to allow food and drink to pass into When we swallow, the LES opens up (the muscle relaxes) so that the food we swallow can enter the stomach Difficulty swallowing liquids or solids, heartburn, regurgitation, and atypical (or noncardiac) chest pain may be symptoms of an esophageal motility disorderComplications specific to an open esophagectomy include less common risks of lung complications, especially pneumonia a severe infection in the chest an injury to the stomach, intestines, lungs, or other organs during surgery a leakage from your esophagus or stomach where the surgeon joined them



Elementary Anatomy And Physiology For Colleges Academies And Other Schools Elementaryanato00hitc Year 1869 5 98 Hitchcock S Anatomy Fig 1 Aplysia Mollusc Laid Open To Show The Viscera A Esophagus E



Esophagus
In species that have undergone detorsion, however, the esophagus may open into the anterior of the stomach, which is the reverse of the usual gastropod arrangement There is an extensive rostrum at the front of the esophagus in all carnivorous snails and slugs 47
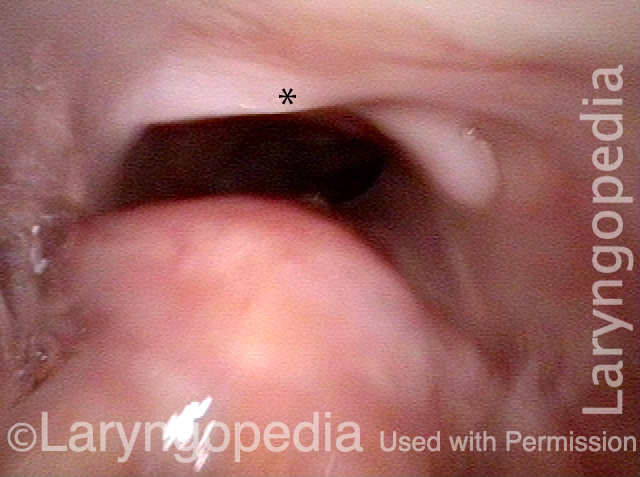



Esophagus Laryngopedia




Miscellaneous Esophagus The Gastrointestinalatlas Gastrointestinalatlas Com
/GettyImages-157583887-59a4a670d963ac001193c73f.jpg)



Esophagus Structure Function And Conditions
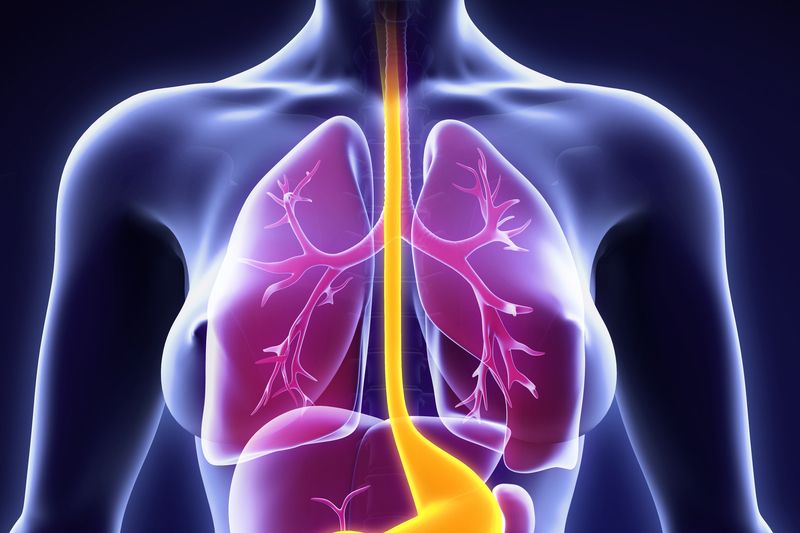



Esophagus Facts Functions Diseases Live Science




What Is Heartburn Sf Center For Acid Reflux
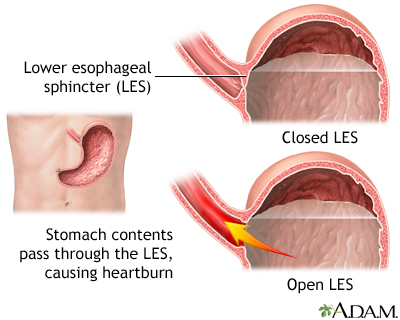



Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease Medlineplus Medical Encyclopedia
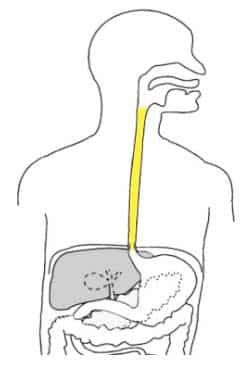



The Oesophagus Location Sphincters Teachmeanatomy
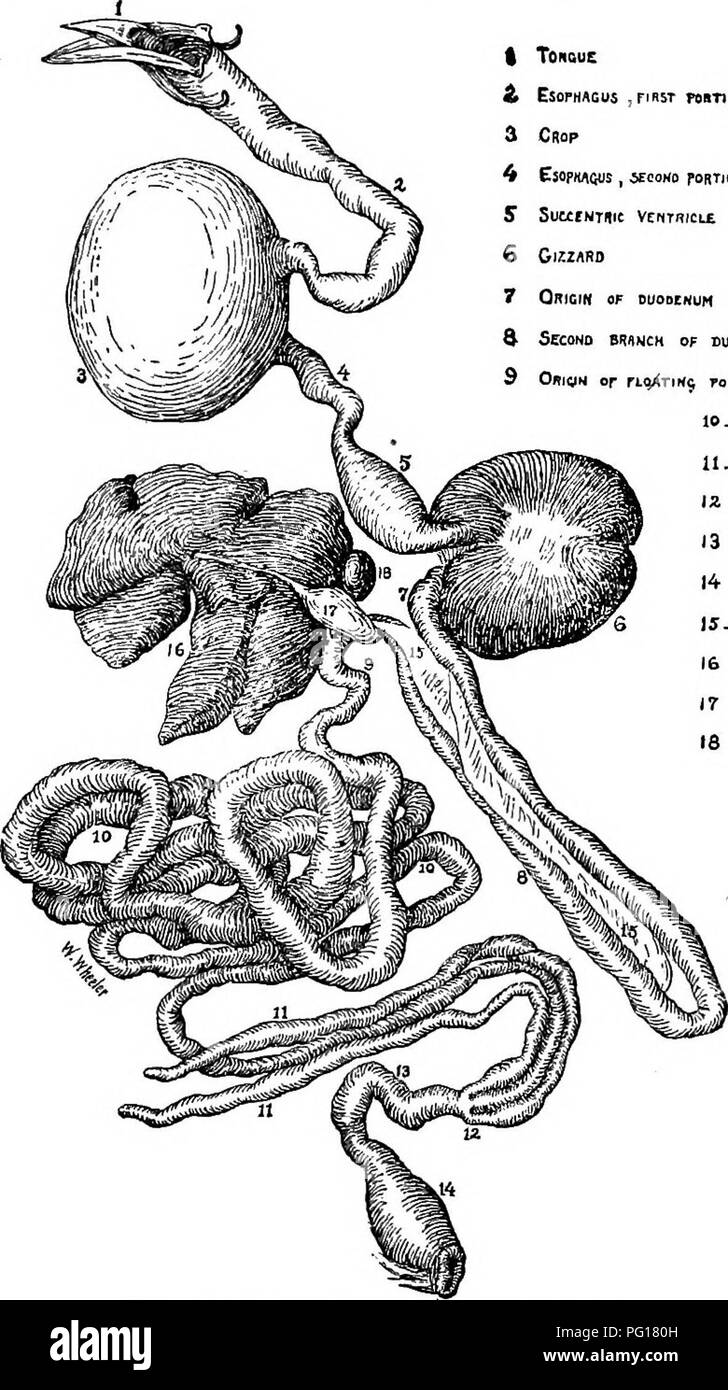



Open Esophagus High Resolution Stock Photography And Images Alamy




Examination Technique And Normal Findings Ento Key
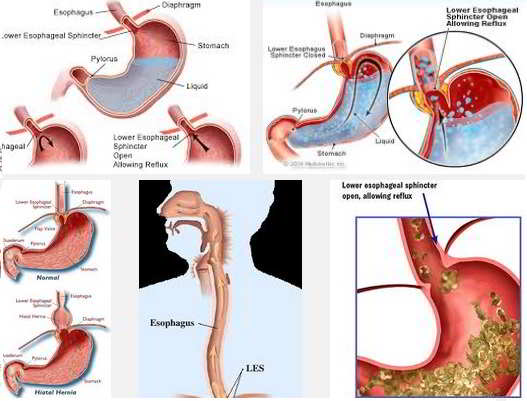



Gastro Esophageal Reflux Disease Gerd Frequently Asked Questions



2
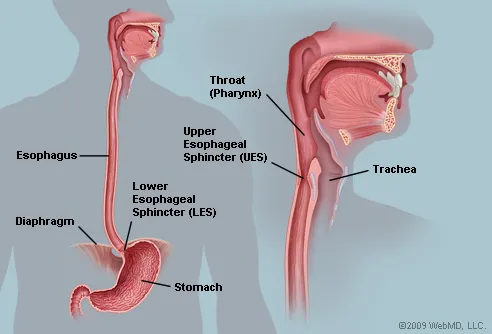



The Esophagus Human Anatomy Picture Function Conditions And More
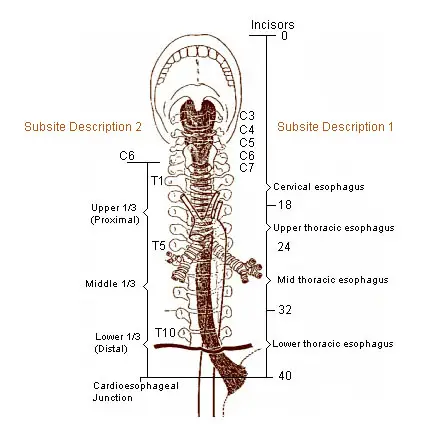



Esophagus Facts Swallowing Reflux Etc Savvy Leo




Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease The Patient Guide To Heart Lung And Esophageal Surgery



E 3 Esophagus
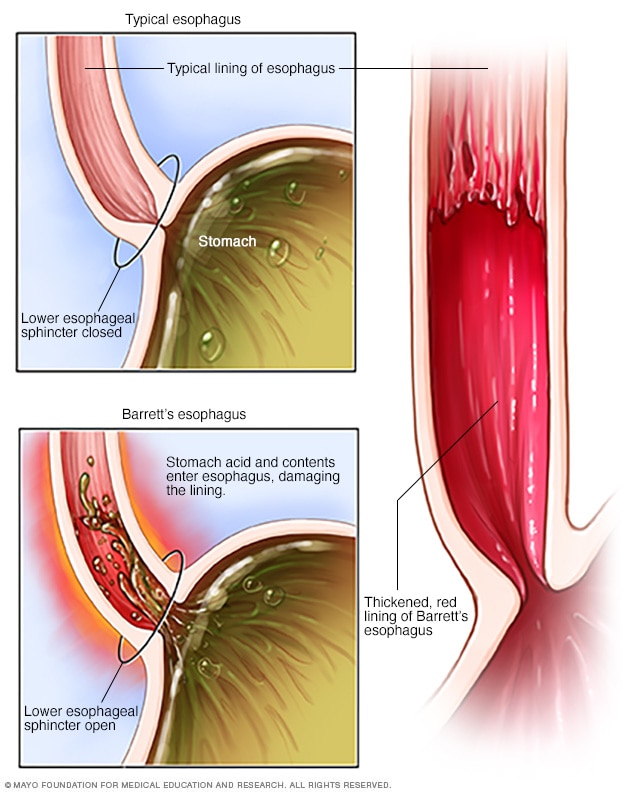



Barrett S Esophagus Symptoms And Causes Mayo Clinic
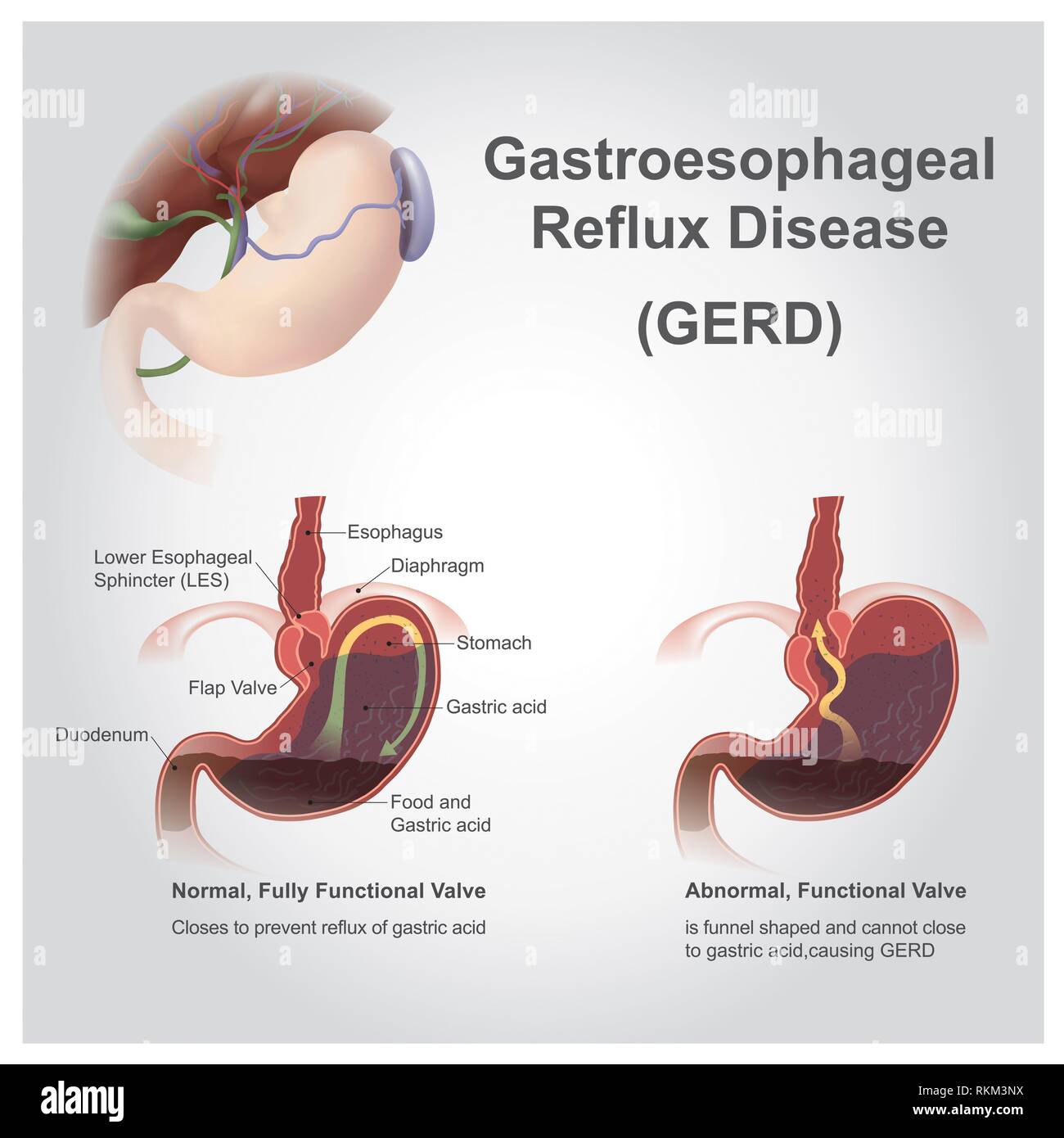



Open Esophagus High Resolution Stock Photography And Images Alamy




Middle Esophagus Particles Are Visible Under Gas Pressure And Fly Download Scientific Diagram




Esophagus Picture Image On Medicinenet Com




Esophagus
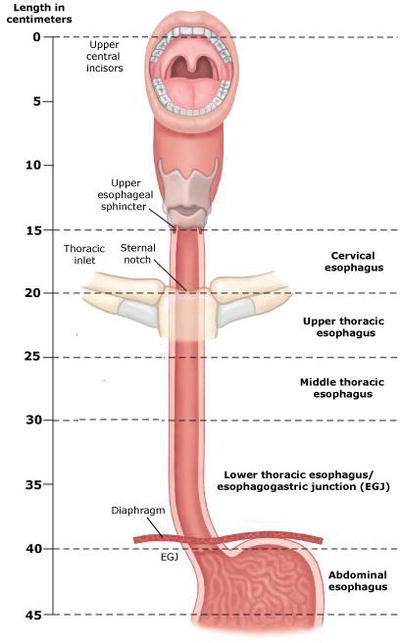



Anatomy Of Esophagus Intechopen




Esophagus Radiology Reference Article Radiopaedia Org



2




Esophagus Wikipedia
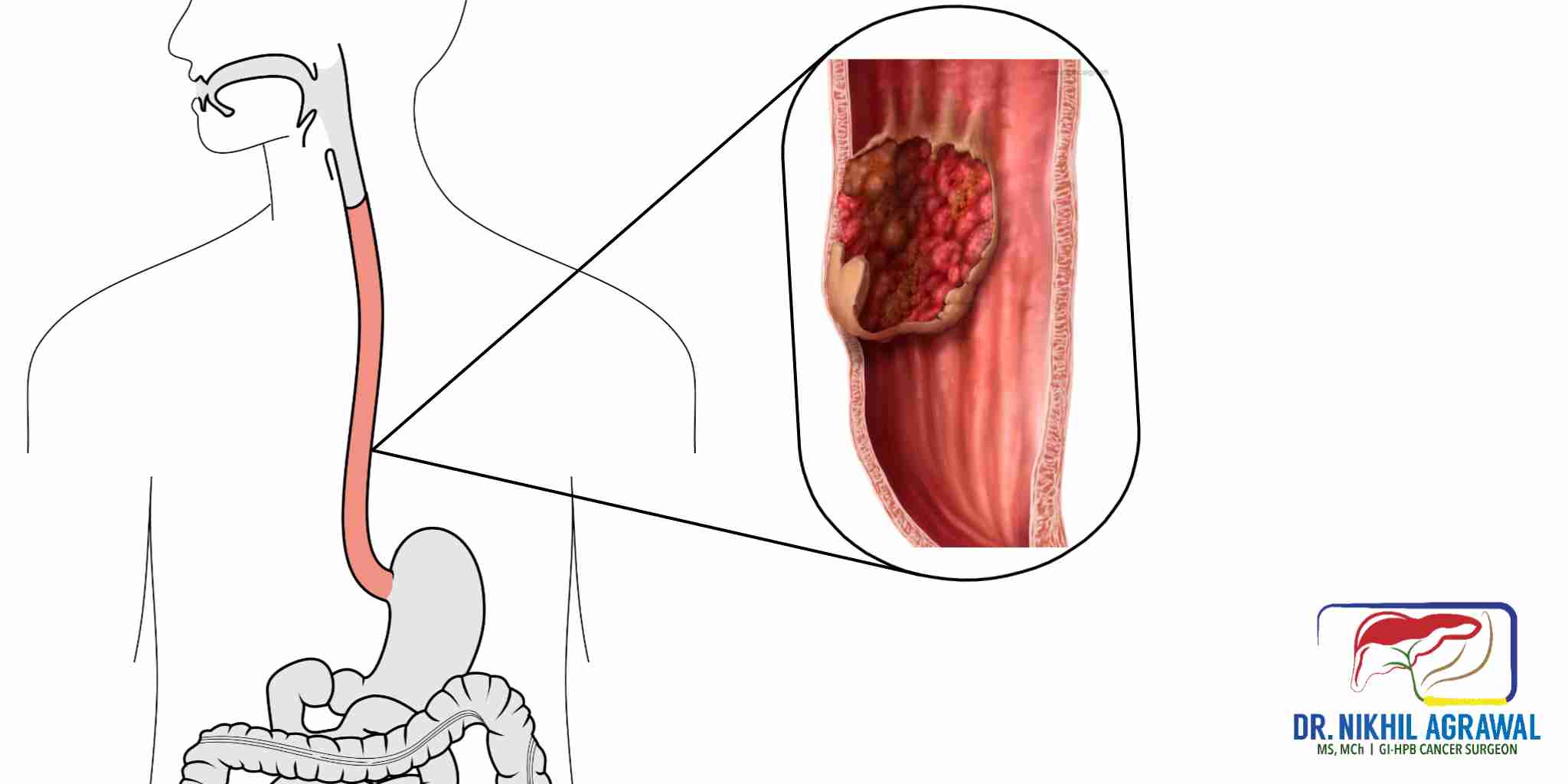



Esophagus Cancer Symptoms Causes Treatment Dr Nikhil Agrawal
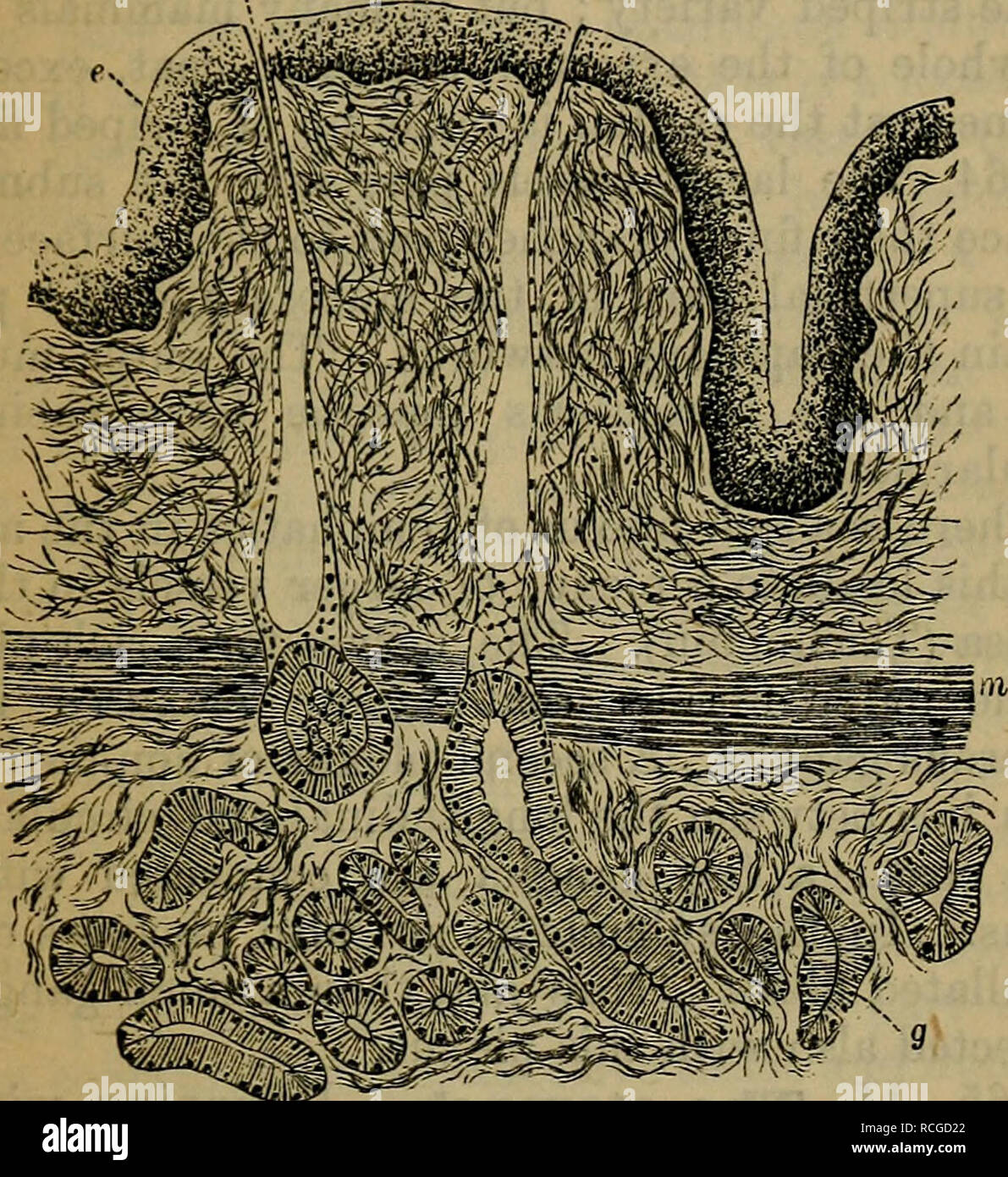



Elements Of Histology Histology Chap Xxiv Esophagus And Stomach 195 Through The Mucosa In Order To Open On The Free Sur Face In Man These Glands Are Relatively Scarce In
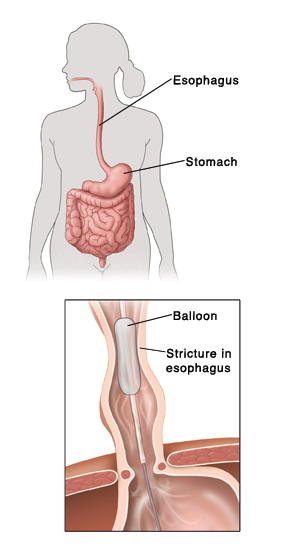



Esophageal Dilation Saint Luke S Health System
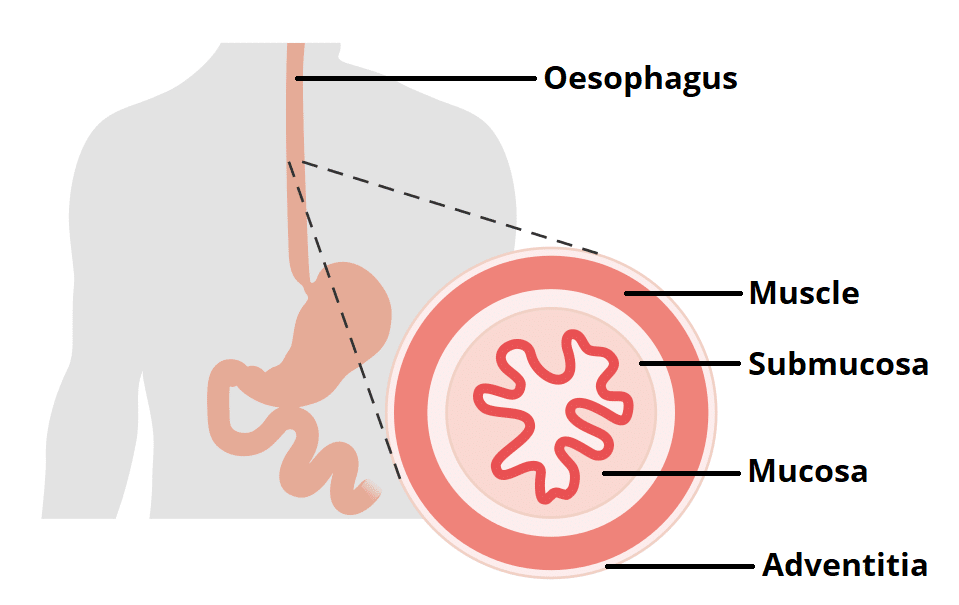



The Oesophagus Location Sphincters Teachmeanatomy
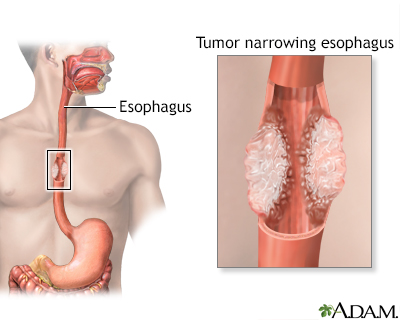



Esophagectomy Open Information Mount Sinai New York
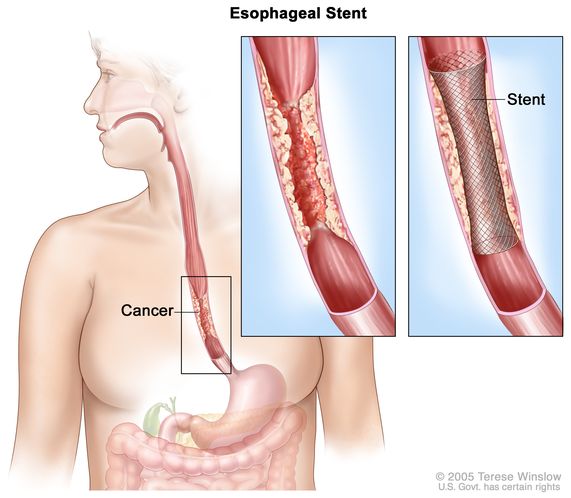



Definition Of Esophageal Stent Nci Dictionary Of Cancer Terms National Cancer Institute




Esophagus Laryngopedia




Acid Reflux Symptoms Remedies Causes Diet Treatment Foods To Avoid




Esophagus Picture Image On Medicinenet Com




8 Use Of A Short Overtube To Splint The Pharynx And Oral Esophagus Download Scientific Diagram
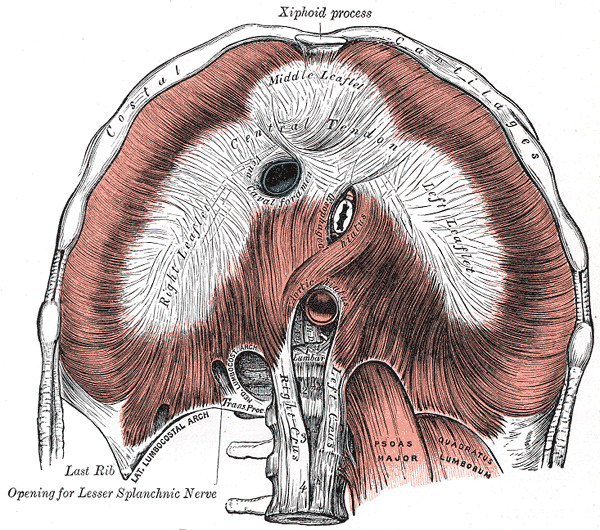



Esophageal Hiatus Wikipedia




Barrett S Esophagus Atlanta Gastroenterology Associates
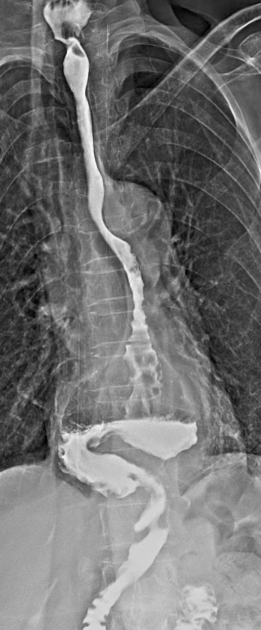



Esophageal Hiatus Radiology Reference Article Radiopaedia Org
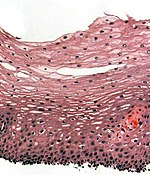



Esophagus Wikipedia
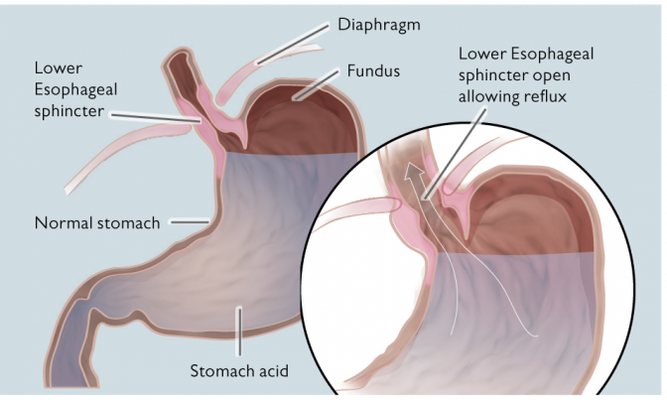



Acid Reflux Implantica




Open Esophagectomy Purpose Procedure Risks




Esophagus Picture Image On Medicinenet Com




Esophageal Sphincter Anatomy Reflux 3d Medical Illustration Stock Vector Illustration Of Gastroesophageal Esophagus




Open Esophagectomy Purpose Procedure Risks
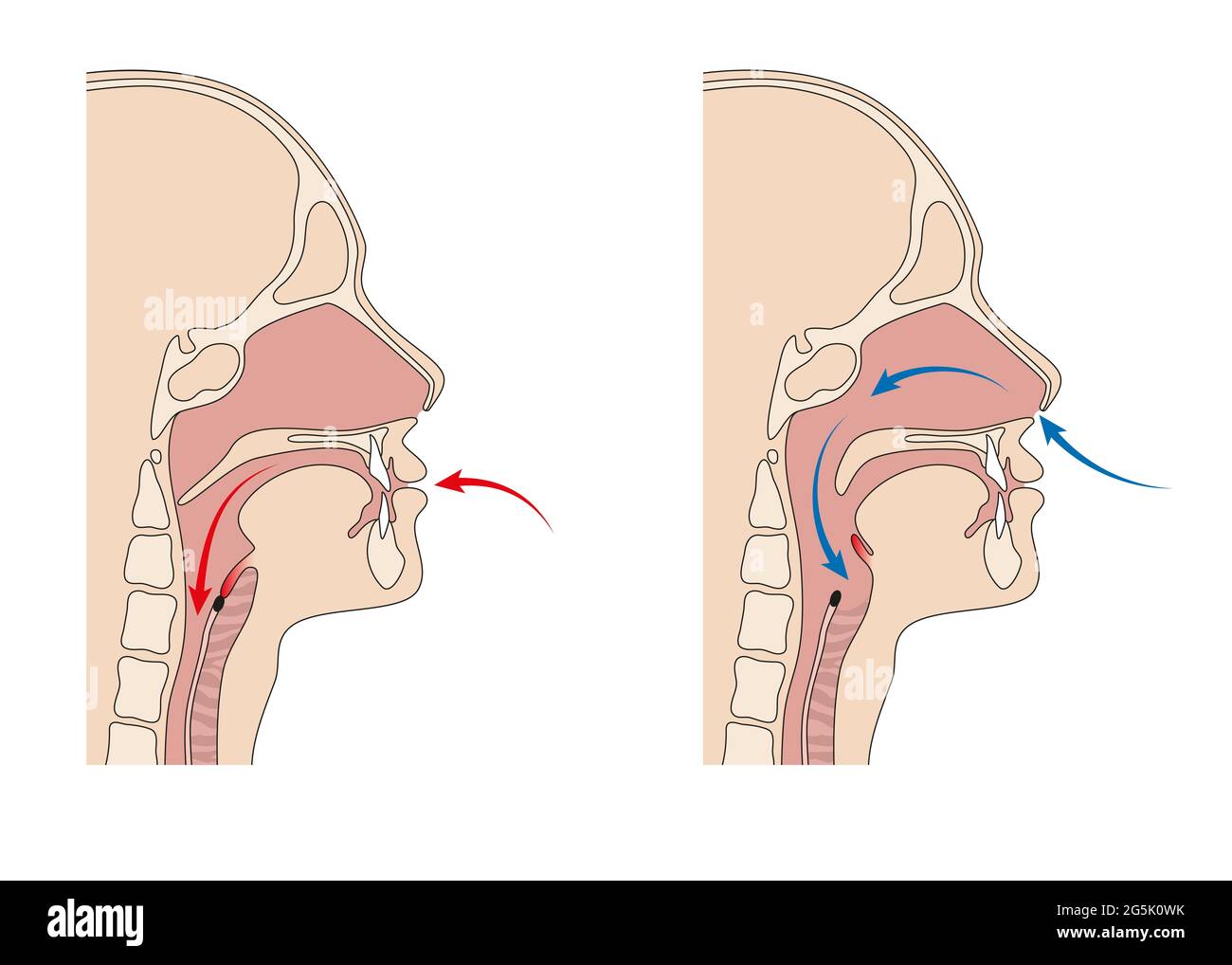



Open Esophagus High Resolution Stock Photography And Images Alamy



Esophagus



Surgery Of The Upper Esophageal Sphincter Open Technique Websurg The E Surgical Reference Of Laparoscopic Surgery Websurg The Online University Of Ircad




Esophagus



2



1
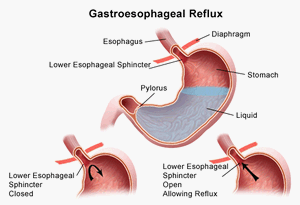



Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease And Heartburn Children S Health Orange County




Anatomy Of Esophagus Intechopen



2




The Esophagus And Its Function Laparoscopic Md



Dr Manohar Lal Sharma Gastroenterologist



3




Esophagus Wikipedia



Esophageal Achalasia Symptoms Diagnosis And Treatment




The Oesophagus Location Sphincters Teachmeanatomy



Dr Mahesh Rao




The Esophagus And Its Function Laparoscopic Md




Open Peroral Endoscopic Myotomy O Poem A Preoperative Barium Download Scientific Diagram



Barrett S Esophagus Musc Health Charleston Sc



Esophagus Wikipedia
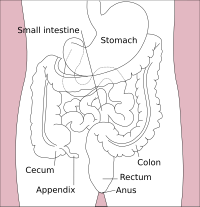



Esophagus Wikipedia
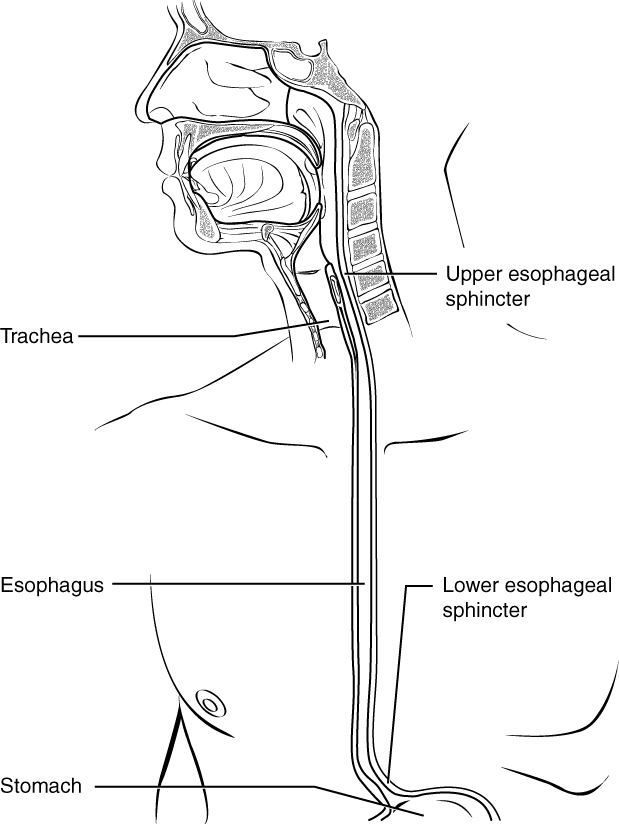



Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease Physiopedia



The Physiology Of Domestic Animals Physiology Comparative Veterinary Physiology Fig 136 Esophageal Canal Open Fig 137 Esophageal Canal Closed Colin By Suture Colin A Inferior Extremity Of The Esophagus B




The Linx Reflux Management System Encircling The Distal Esophagus In Download Scientific Diagram




Beef Chomper Flattened Esophagus Open Range Pet Treats




Barrett S Esophagus Symptoms Causes Treatment Risks Dysplasia



2




Esophagus Anatomy And Development Gi Motility Online
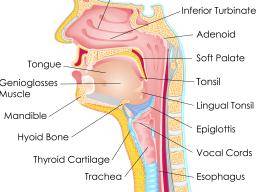



Esophageal Achalasia Symptoms Diagnosis And Treatment




Plain Chest Radiograph Showing An Open Safety Pin In The Upper Third Of Download Scientific Diagram




Dr Ahmed Adel Clinic Added A New Dr Ahmed Adel Clinic
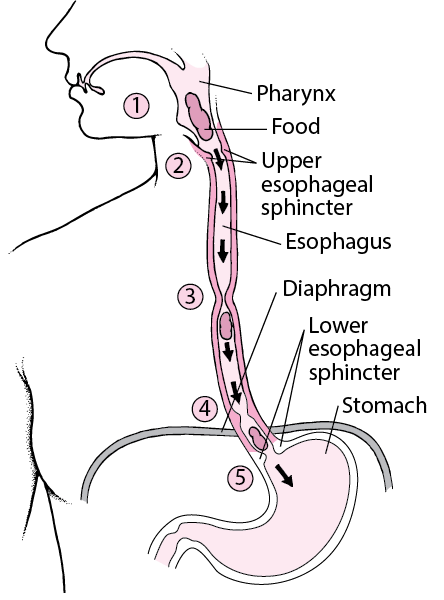



Overview Of The Esophagus Digestive Disorders Merck Manuals Consumer Version
/GettyImages-155358910-73a8fc2964a54b14a84e9fe04816a6e8.jpg)



Esophagus Anatomy Function And Treatment
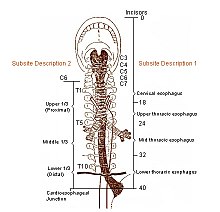



Esophagus Wikipedia
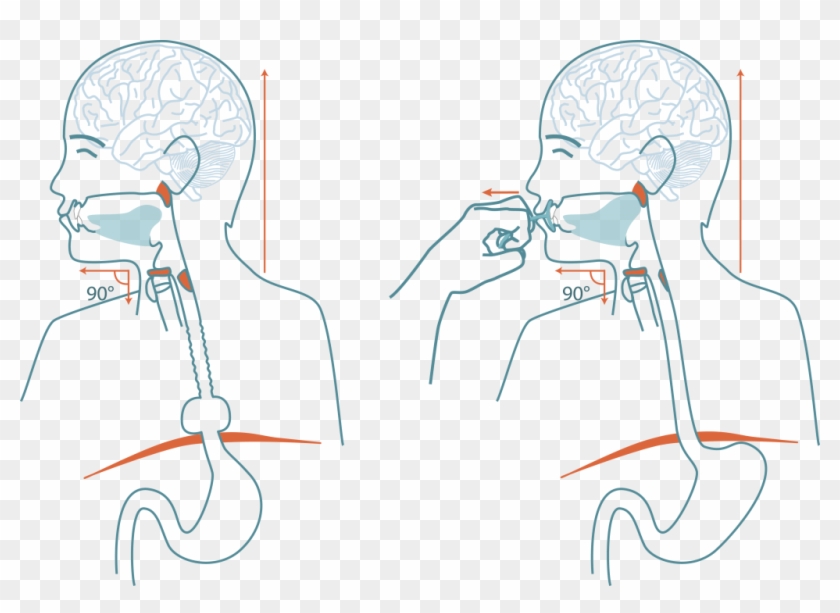



See How The Upper Esophagus Sphincter Does Not Open Cartoon Hd Png Download 1024x699 Pngfind



Esophageal Achalasia Symptoms Diagnosis And Treatment



2
/GettyImages-165564610-5a60a646c7822d0037df638b.jpg)



Upper Esophageal Sphincter Function And Acid Reflux Pain




Pin On Good To Know



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿